Manufacturing a PP woven sack
Learn and understand the intricate process of manuacturing woven sacks and Adpack how sits at the forefront of packaging innovation when it comes to the manufacturing of woven packaging
Discover Our PP Woven Bags Manufacturing Journey
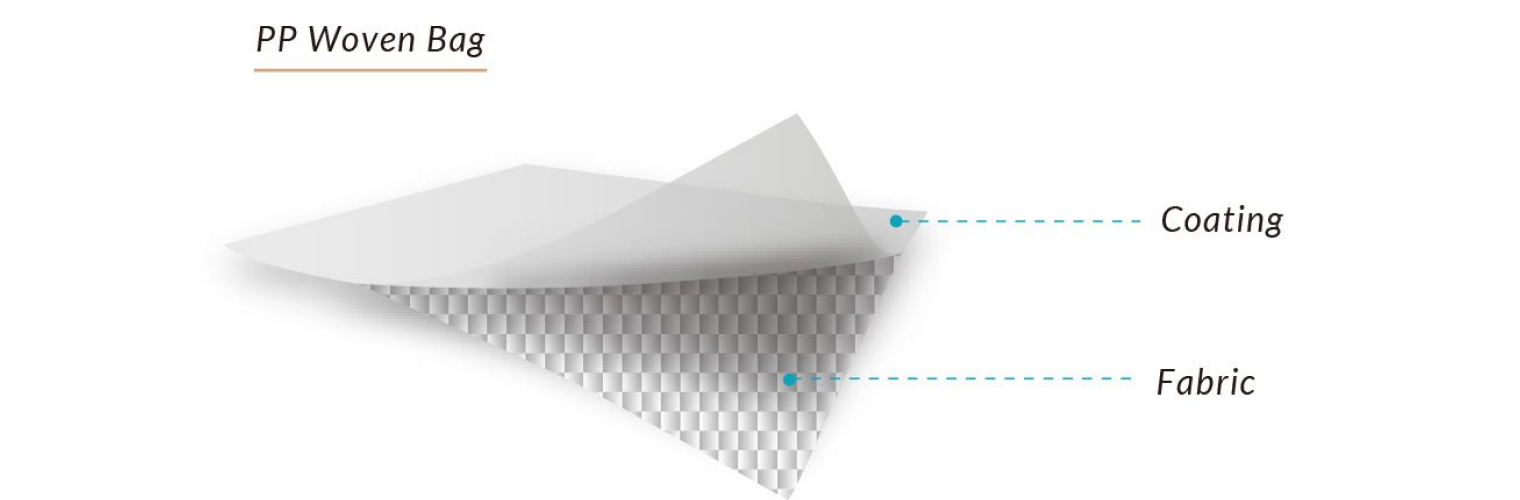
Overview of Polypropylene Weaving and PP Woven Bags Production Dive into the intricate process of crafting PP woven bags and related packaging solutions, focusing on the use of polypropylene woven fabric. At Adpack, we utilize top-quality polypropylene (PP) resin to fabricate robust woven fabrics, subsequently transformed through printing, cutting, and stitching into versatile bags of diverse styles and dimensions. We uphold the highest standards of quality control and environmental responsibility, ensuring that our bags are not only reusable and recyclable but also crafted from sustainable materials. Leveraging advanced technology and skilled artisans, we are committed to delivering superior quality and eco-friendly BOPP bags.
Our Comprehensive 10-Step Production Process for PP Woven Bags The creation of our PP woven bags is a meticulously managed sequence of steps, designed to produce robust and multifunctional bags, embodying our continuous quest for process enhancement:
- Step 01
Choosing the Right Raw Materials for PP Woven Bags
Raw Material: Polypropylene materials can be found in both powder and particle/granule forms. Adpack uses granulated polypropylene and blends it with a variety of additives and modifying materials to enhance material stability and provide other advanced properties. A material like CaCO3 is especially important because it not only improves the efficiency of the production, adds whiteness but also reduces cost – whilst most reputable manufacturers will only use a small amount of this additive many manufacturers will overload with CaCO3 in order to reduce their cost but adding too much will weaken the bags so customers should be careful when comparing products and always work with trusted/reputable manufacturers. Additionally many manufacturers will use recycled or sub-grade polypropylene in their production. Adpack only uses premium-grade polypropylene (PP) resin, known for its durability and strength. Here are some examples of other additives that may be used in the manufacturing process where relevant or necessary:
- UV Stabilizers: These additives are essential for protecting the bags from the harmful effects of prolonged exposure to sunlight, which can cause the material to degrade and become brittle.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants if required can play a role in preventing the deterioration of the polypropylene resin due to heat, oxygen, and other environmental factors, thereby extending the lifespan of the bags.
- Slip and Anti-block Agents: Slip agents reduce friction, making the bags smoother and easier to handle during production, transportation, and storage. Anti-block agents prevent the bags from sticking together, particularly in high humidity conditions, ensuring easy separation and handling.
- Colorants: Pigments and dyes are used to provide vibrant colors and enhance the visual appeal of the bags, allowing for customization according to client specifications.
- Flame Retardants: These additives reduce the flammability of the bags, making them safer to use in various environments.

- Step 02
Melting & Extruding PP Resin and other Raw Materials
After the correct raw materials are chosen they are added to the CDMU, a specialized equipment that allows raw materials to be accurately fed into the machinery; Adpack uses a CDMU that has the capacity to get to 0.1% levels of accuracy. Once the CDMU is loaded its advanced programming takes over and it feeds the various pelletized raw materials into the extruder. The extruder containing a specalised bi-metallic screw is a machine that heats and mixes all the resins to above their melting points, typically between 180-250°C (356-482°F). The precise temperature depends on the specific type of resin, the extrusion equipment, and the desired properties of the final product. During this process, the resin is melted uniformly to avoid any degradation that could lead to color changes, reduced strength, or brittleness. The melted resin is then forced through a die to form a flat sheet which is then slit into long, continuous flat tapes, which are essential for the weaving process.
NB: Important parameters include blending ratios, draft and inflation ratios, breaking force, linear density, and dimension tolerance, ensuring high-quality tapes for weaving.

- Step 03
Weaving the Fabric
After the PP resin is melted and extruded into tapes, these tapes are collected on “cheese” pipes and then taken to the weaving looms. In this high speed machine also known as a circular weaving machine the tapes are woven together in a specialized pattern to form a strong and durable fabric. Adpack’s weaving is done using state-of-the-art circular weaving loom machines, which ensure minimal defects and high productivity. The weaving process includes several key steps:
Warping: PP tapes or flat yarns are wound onto a warp beam to create the warp, the set of parallel yarns that run the length of the fabric.
Shedding: The warp is passed through a shedding device, which creates an opening or “shed” between the upper and lower layers of the warp, allowing weft yarns to be inserted.
Weft Yarn Insertion: Weft yarns or tapes are inserted through the shed using shuttles or circular looms, interlacing with the warp yarns to create the woven polypropylene pattern.
Beating-up: A comb-like device called the “reed” pushes the weft yarns tightly together, creating a tightly woven fabric.
Repetition: These steps are repeated to achieve the desired fabric width and length. This tightly woven fabric forms the foundation for our BOPP and woven bags.
Quality Control: Fabric being woven is constantly inspected by the operator to ensure that no defects pass onto the next stage and eventually the customer
NB: Key factors include weaving density, tensile strength, unit weight per square meter, and width. These parameters affect the fabric’s strength, load capacity, and suitability for various applications.

- Step 04
Printing and Lamination
Once the woven fabric is produced, it can if required be sent for lamination which can be used to further enhance its properties. Lamination involves applying another layer of polymer film on top of the fabric roll; this can be further enhanced with a layer of BOPP (biaxially oriented polypropylene) lamination film, which can be pre-printed with specialized blended inks to provide a high graphic look to the end product. At this stage there is also another quality inspection process to ensure that all the printing is 100% perfect.
After lamination (or if unlaminated then directly) the fabric goes for printing. the printing process involves several stages:
Pre-press Preparation: Specialized graphic design software is used to create the text, images, and logos that will be printed on the bags. The final design is converted into a printable format, such as a digital file or plate.
Flexographic and Rotogravure Printing: Two common methods are used for printing on woven sacks. Flexographic printing uses flexible plates, while rotogravure printing uses engraved cylinders. Both methods allow for high-quality, customizable prints.
Plate Creation: For traditional flexographic or gravure printing, plates are created from the design, usually made of metal or other materials, and mounted onto the printing press. This can take up to 72hrs.
Ink Preparation: Ink is mixed to the required color and viscosity specifications.
Printing: The woven bags are fed into the press, where the ink is transferred onto the bags using the plates or cylinders. This process is repeated for each color layer.
Drying and Curing: The ink is dried or cured after each application to ensure durability.
Post-press Finishing: Additional treatments such as heat-setting, varnishing, or coating may be applied for added protection or glossiness.
Quality Control: Throughout the printing process, strict quality control measures ensure color accuracy, print clarity, and overall quality, addressing any defects immediately.
NB: Important factors include temperature control, coating pressure, and peeling strength to ensure high-quality laminated fabrics.
- Step 05
Cutting of Fabric Rolls into Bags
The woven fabric is cut into the desired shapes and sizes for bag production. This can be done using heat cutting or cold cutting methods:
Heat Cutting: A hot knife or heated wire melts and seals the fabric edges, creating clean and sealed cuts. This method involves precise temperature control to avoid excessive melting or scorching.
Cold Cutting: A knife or blade mechanically cuts the fabric without heat, suitable for coated materials. Cold cutting reduces energy consumption and fraying, while maintaining the strength and durability of the fabric. Both methods ensure that the cuts are accurate, clean, and defect-free, preparing the fabric for the sewing process.
- Step 06
Sewing and Hemming
At Adpack, we employ state-of-the-art automatic cutting and sewing machines that revolutionize our production process. These advanced systems seamlessly integrate steps 5 and 6 of manufacturing, transforming raw fabric rolls into finished bags in one fluid operation. As the fabric feeds through, it’s precisely cut, skillfully folded, and securely sewn—all in a single, efficient process.
For enhanced functionality, we offer gusseting during this stage, allowing bags to stand upright when filled, a feature particularly valued in industrial and agricultural applications. Our commitment to quality is unwavering; we’ve implemented a rigorous inspection process that runs concurrent with cutting and sewing. This system instantly identifies any bags that don’t meet our exacting standards, flagging them for immediate correction or replacement.
This approach not only streamlines production but also significantly reduces the possibility of defects reaching our customers, ensuring each Adpack bag delivers the superior performance our clients expect.
Folding: The fabric after cutting is then folded at the bottom to form the bottom of the bag.
Stitching: The folded portion of the bag is then sewn; sewing begins at the beginning of the bag, moving along the bottom side with reinforced stitching for added strength.
Handles or Liner Hemming: Handles are attached according to the design specifications and sewn to the bag; in the case of liners which may be preinserted they are also hemmed at this stage
Finishing: Any excess threads are trimmed, and the bags undergo quality checks for any loose stitches or flaws.

- Step 07
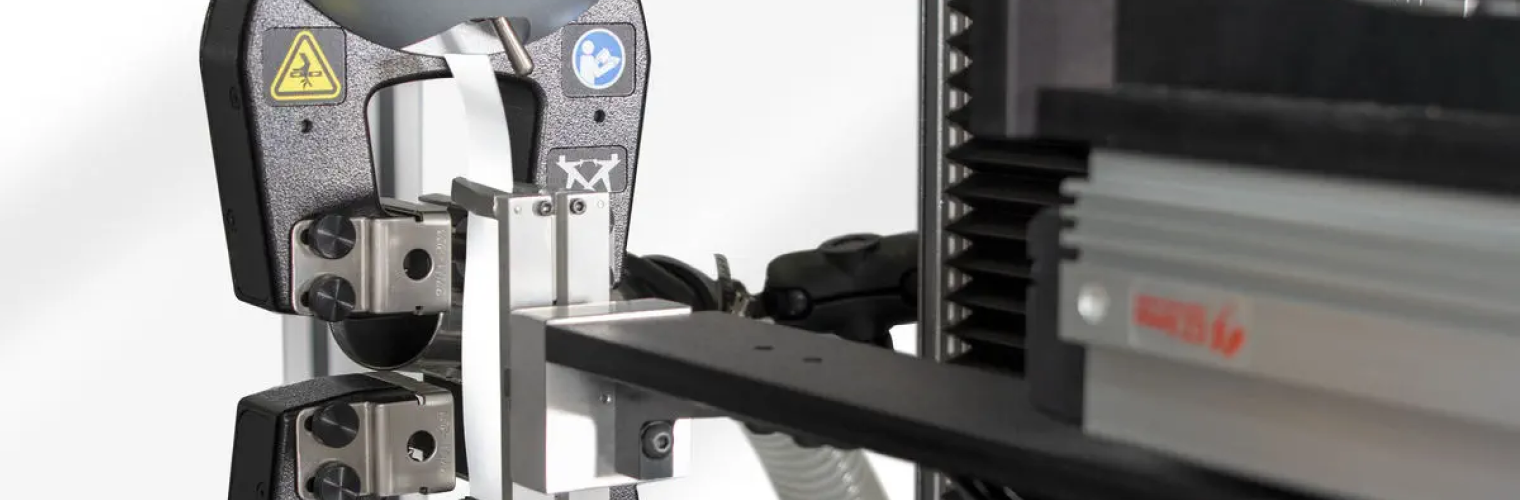
Quality Control
At Adpack, we are dedicated to maintaining the highest standards of quality through a meticulous inspection process at every stage of production. Before a bag leaves our factory, it undergoes a comprehensive evaluation by our trained specialists. They carefully examine critical elements such as polymer melt flow, material composition, and weaving integrity. Additionally, we ensure that stitching points are inspected, handles are precisely aligned, lamination adhesion strength is verified, and printing clarity and overall aesthetic appeal are assessed. This thorough examination ensures that every product leaving our facility meets our stringent quality standards. Any detected imperfections are immediately addressed, ensuring that only flawless bags reach our customers.

- Step 08
Packaging and Baling
Once approved, the bags are systematically organized for efficient distribution. They are carefully counted and bundled into manageable packs for onward consolidation into larger bales of 500 pieces. Each bale is securely wrapped in a protective cover and tightly strapped, safeguarding the products during transportation and storage. This meticulous approach to packaging not only preserves the quality of our bags but also facilitates easy handling and inventory management for our clients. The finished bags are stored in a secure and controlled environment prior to transportation. Double baling is available at an additional cost.

